Language Arts & Disciplines
Language Arts & Disciplines Books
Sort by:
by:
Dale Carnagey
CHAPTER I ACQUIRING CONFIDENCE BEFORE AN AUDIENCE There is a strange sensation often experienced in the presence of an audience. It may proceed from the gaze of the many eyes that turn upon the speaker, especially if he permits himself to steadily return that gaze. Most speakers have been conscious of this in a nameless thrill, a real something, pervading the atmosphere, tangible, evanescent,...
more...
INTRODUCTION. So many slighting remarks have been made of late on the use of teaching grammar as compared with teaching science, that it is plain the fact has been lost sight of that grammar is itself a science. The object we have, or should have, in teaching science, is not to fill a child's mind with a vast number of facts that may or may not prove useful to him hereafter, but to draw out and...
more...
Word study and English grammar are important to the young printer for several reasons. In the first place, disregard of the correct use and combination of words is a distinct mark of inferiority and a serious bar to business and social advancement. A man's use of words is commonly taken as a measure of his knowledge and even of his intelligence. Carelessness in this regard often causes a man to be...
more...
by:
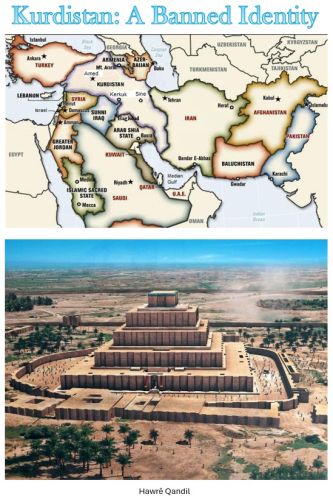
Hawre Qandil
Kurdistan: A Banned Identity is a powerful historical, political, and cultural study that uncovers the systematic suppression of Kurdish identity across centuries of domination, denial, and forced assimilation. This book confronts the silence imposed on one of the Middle East’s oldest indigenous nations and restores a history that has been deliberately erased, distorted, or forbidden. Drawing on...
more...
by:
Thomas Wood
Page v PREFACE This book was begun as a result of the author's experience in teaching some classes in English in the night preparatory department of the Carnegie Technical Schools of Pittsburg. The pupils in those classes were all adults, and needed only such a course as would enable them to express themselves in clear and correct English. English Grammar, with them, was not to be preliminary to...
more...
CHAPTER I. GERMANIC ORIGIN OF THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE.—DATE. § 1. The first point to be remembered in the history of the English language, is that it was not the primitive and original tongue of any of the British Islands, nor yet of any portion of them. Indeed, of the whole of Great Britain it is not the language at the present moment. Welsh is spoken in Wales, Manks in the Isle of Man, and Scotch...
more...
by:
Joseph Devlin
CHAPTER I REQUIREMENTS OF SPEECH Vocabulary—Parts of Speech—Requisites It is very easy to learn how to speak and write correctly, as for all purposes of ordinary conversation and communication, only about 2,000 different words are required. The mastery of just twenty hundred words, the knowing where to place them, will make us not masters of the English language, but masters of correct speaking and...
more...
ENGLISH A COMPOSITE LANGUAGE “A very slight acquaintance with the history of our own language will teach us that the speech of Chaucer’s age is not the speech of Skelton’s, that there is a great difference between the language under Elizabeth and that under Charles the First, between that under Charles the First and Charles the Second, between that under Charles the Second and Queen Anne; that...
more...
PREFACE. Almost every English boy can be taught to write clearly, so far at least as clearness depends upon the arrangement of words. Force, elegance, and variety of style are more difficult to teach, and far more difficult to learn; but clear writing can be reduced to rules. To teach the art of writing clearly is the main object of these Rules and Exercises. Ambiguity may arise, not only from bad...
more...
PREFACE In July, 1898, I presented at the National Educational Association, convened in Washington, a Course of Study in English. At Los Angeles, in 1899, the Association indorsed the principles of this course, and made it the basis of the Course in English for High Schools. At the request of friends, I have prepared this short text-book, outlining the method of carrying forward the course, and...
more...